Icy Lunar Regolith Simulants
The main objective of this master thesis is to determine the influence of ice content on the strength and stiffness of soil material on the moon.

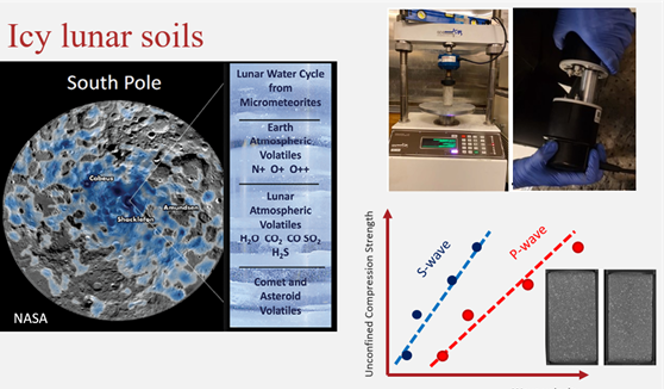
Human development on the lunar surface depends on our ability to extract water ice from within the lunar near surface. Water is critical not just to sustain life but also to produce rocket fuel and aid construction processes.
Recently, it was discovered that water ice (up to 30% by weight) is present in some permanently shadowed craters within the lunar polar regions. These regions thus provide exciting targets for In Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU).
Today, the composition of the icy regolith and the quantity of ice available – key parameters to determine the resource potential and design excavation tools – remain unclear.
As preparations begin for new missions to the Moon (e.g., ESA's EL3 and NASA's Artemis), and with ISRU and space tourism expected to follow, the need to understand and map the characteristics and amount of icy regolith on the lunar surface is growing.
The assignment
This project aims to determine icy lunar regolith simulants' geo-mechanical and geophysical characteristics.
The student will help perform geophysical and geotechnical laboratory tests at sub-zero temperatures and consider samples with a wide range of variations, such as regolith type, initial ice content, relative density, and initial fabric of the interparticle regolith.
As part of this study, 3D CT scans will be acquired and post-processed. A key research goal is to determine the main parameters that control the strength of icy regolith.
During this project, the student will learn how to:
- perform geotechnical and geophysical laboratory tests, including quality control and uncertainty quantification; potentially also modify testing equipment
- process and interpret geotechnical and geophysical laboratory tests
- collect 3D micro-CT scan data and carry out 3D image analysis
- synthesize test results concerning the scientific literature
- effectively communicate the results of geotechnical and geophysical tests through visual, written, and oral forms
- characterize and quantify frozen-soil
- work within a multidisciplinary and international team
Primary research questions
- How do Lunar regolith simulants behave at various levels of water ice concentration?
- What are the main differences in the geotechnical and geophysical properties of icy Lunar simulants?
- What are the effects of ice form distribution on the geotechnical and geophysical properties?
